7.3 DOM nodes Part 1¶
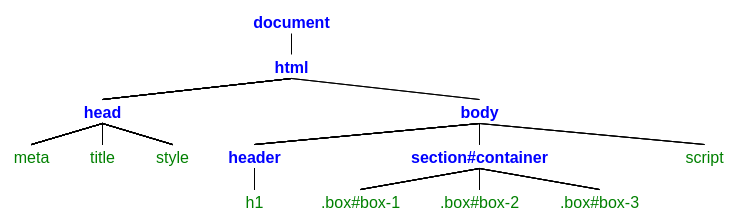
In this lesson; we will be using the following HTML document:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" dir="ltr">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Three Magical boxes</title>
<style>
#container{
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.box{
width: 10rem;
height: 10rem;
margin: 1rem;
}
#box-1{
background: lightblue;
}
#box-2{
background: Olive;
}
#box-3{
background: tomato;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<header>
<h1>Welcome to 3 three magical boxes website</h1>
</header>
<section id="container">
<div class="box" id="box-1"></div>
<div class="box" id="box-2"></div>
<div class="box" id="box-3"></div>
</section>
<script src="script.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
DOM Nodes
There are 12 node types, some of them are:
| Node Type | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Node.ELEMENT_NODE | 1 | An element node like <div> or <h1> |
| Node.ATTRIBUTE_NODE | 2 | An attribute of an element |
| Node.TEXT_NODE | 3 | The text inside an element or attribute. |
| Node.COMMENT_NODE | 8 | A comment node <!-- comment here --> |
Element Node¶
Task 1: Get the element whose id equals to container.
let container = document.getElementById("container");
console.log(container);
The result is: <section id="container">...</section>
Task 2: Get the first section tag.
let firstSection = document.getElementsByTagName("section")[0];
console.log(firstSection);
The result is: <section id="container">...</section>
Task 3: Get the element whose id equals to container using querySelector.
let container = document.querySelector("#container");
console.log(container);
The result is: <section id="container">...</section>
Task 4: Get the first section tag using querySelectorAll.
let firstSection = document.querySelectorAll("section")[0];
console.log(firstSection);
The result is: <section id="container">...</section>
Many ways to get an element?
Yes! You can access an HTML element using different methods. Use what sounds more convenient and easy for you.
Task 5: Refer to task 4; what is the result of firstSection.nodeName?
let firstSection = document.querySelectorAll("section")[0];
console.log(firstSection.nodeName);
The result is: SECTION
nodeName
The nodeName property returns the name of the node.
Task 6: Refer to task 4; what is the result of firstSection.nodeType?
let firstSection = document.querySelectorAll("section")[0];
console.log(firstSection.nodeType);
The result is: 1
nodeType
The nodeType property returns a number that identifies what the node is.
Task 7: Get all the box elements. Use any method you prefer.
let boxes = document.getElementsByClassName("box");
console.log(boxes);
The result is: HTMLCollection(3) [div#box-1.box, div#box-2.box, div#box-3.box...]
Task 8: Get the first child of the container.
let container = document.getElementById("container");
let fstChildEl = container.children[0];
console.log(fstChildEl);
The result is: <div id="box-1" class="box"></div>
Task 9: Get the first child of the container using firstElementChild.
let container = document.getElementById("container");
let fstChildEl = container.firstElementChild;
console.log(fstChildEl);
The result is: <div id="box-1" class="box"></div>
firstElementChild
The firstElementChild returns the first child element node of the parent.
Task 10: Refer to task 9; what is the node name of the fstChildEl node?
let container = document.getElementById("container");
let fstChildEl = container.firstElementChild;
console.log(fstChildEl.nodeName);
The result is: DIV
Task 11: Refer to task 9; what is the node type of the fstChildEl node?
let container = document.getElementById("container");
let fstChildEl = container.firstElementChild;
console.log(fstChildEl.nodeType);
The result is: 1
Task 12: Get the last child of the container.
let container = document.getElementById("container");
let lstChildEl = container.children[2];
console.log(lstChildEl);
The result is: <div id="box-3" class="box"></div>
Task 13: Get the last child of the container using lastElementChild.
let container = document.getElementById("container");
let lstChildEl = container.lastElementChild;
console.log(lstChildEl);
The result is: <div id="box-3" class="box"></div>
lastElementChild
The lastElementChild returns the last child element node of the parent.
Task 14: Refer to task 13; what is the node name of the lstChildEl node?
let container = document.getElementById("container");
let lstChildEl = container.lastElementChild;
console.log(lstChildEl.nodeName);
The result is: DIV
Task 15: Refer to task 13; what is the node type of the lstChildEl node?
let container = document.getElementById("container");
let lstChildEl = container.lastElementChild;
console.log(lstChildEl.nodeType);
The result is: 1
Task 16: Get the second child of the container.
let container = document.getElementById("container");
let secondChild = container.children[1];
console.log(secondChild);
The result is: <div id="box-2" class="box"></div>
Task 17: Refer to task 16; get the previous sibling element of the secondChild element. Use previousElementSibling.
let container = document.getElementById("container");
let secondChild = container.children[1];
let previousSibling = secondChild.previousElementSibling;
console.log(previousSibling);
The result is: <div id="box-1" class="box"></div>
previousElementSibling
The previousElementSibling property returns the element prior to the specified one.
Task 18: Refer to task 17; what is the node name of the previousSibling node?
let container = document.getElementById("container");
let secondChild = container.children[1];
let previousSibling = secondChild.previousElementSibling;
console.log(previousSibling.nodeName);
The result is: DIV
Task 19: Refer to task 17; what is the node type of the previousSibling node?
let container = document.getElementById("container");
let secondChild = container.children[1];
let previousSibling = secondChild.previousElementSibling;
console.log(previousSibling.nodeType);
The result is: 1
Task 20: Refer to task 16; get the next sibling element of the secondChild element. Use nextElementSibling.
let container = document.getElementById("container");
let secondChild = container.children[1];
let nextSibling = secondChild.nextElementSibling;
console.log(nextSibling);
The result is: <div id="box-3" class="box"></div>
nextElementSibling
The nextElementSibling property returns the element following the specified one.
Task 21: Refer to task 20; what is the node name of the nextSibling node?
let container = document.getElementById("container");
let secondChild = container.children[1];
let nextSibling = secondChild.nextElementSibling;
console.log(nextSibling.nodeName);
The result is: DIV
Task 22: Refer to task 20; what is the node type of the nextSibling node?
let container = document.getElementById("container");
let secondChild = container.children[1];
let nextSibling = secondChild.nextElementSibling;
console.log(nextSibling.nodeType);
The result is: 1
Attribute Node¶
hasAttribute()¶
Task 23: Get the third box.
let box3 = document.getElementById("box-3");
console.log(box3);
The result is: <div id="box-3" class="box"></div>
Task 24: Refer to task 23; does box3 element has a class attribute. Hint: use element.hasAttribute("class").
let box3 = document.getElementById("box-3");
let hasClass = box3.hasAttribute("class");
console.log(hasClass);
The result is: true
element.hasAttribute()
The element.hasAttribute() method returns an either true or false value indicating whether the element has the specified attribute or not.
Task 25: Refer to task 23; does box3 element has an id attribute. Hint: use element.hasAttribute("id").
let box3 = document.getElementById("box-3");
let hasId = box3.hasAttribute("id");
console.log(hasId);
The result is: true
Task 26: Refer to task 23; does box3 element has a title attribute. Hint: use element.hasAttribute("title").
let box3 = document.getElementById("box-3");
let hasTitle = box3.hasAttribute("title");
console.log(hasTitle);
The result is: false
getAttribute()¶
Task 27: Get the #box-1 element in the #container element.
let box1 = document.querySelector("#container #box-1");
console.log(box1);
The result is: <div id="box-1" class="box"></div>
Task 28: Refer to task 27; does box1 has a class attribute?
let box1 = document.querySelector("#container #box-1");
let hasClass = box1.hasAttribute("class");
console.log(hasClass);
The result is: true
Task 29: Refer to task 27; what is the value of the class attribute? Hint: use getAttribute("class").
let box1 = document.querySelector("#container #box-1");
let classValue = box1.getAttribute("class");
console.log(classValue);
The result is: box
element.getAttribute()
The element.getAttribute() method returns the value of the specified attribute of the given element.
If the element does not have the specified attribute, The element.getAttribute() method returns null or an empty string "".
Task 30: Refer to task 27; does box1 has an id attribute?
let box1 = document.querySelector("#container #box-1");
let hasId = box1.hasAttribute("id");
console.log(hasId);
The result is: true
Task 31: Refer to task 27; what is the value of the id attribute?
let box1 = document.querySelector("#container #box-1");
let idValue = box1.getAttribute("id");
console.log(idValue);
The result is: box-1
Task 32: Refer to task 27; does box1 has an alt attribute?
let box1 = document.querySelector("#container #box-1");
let hasAlt = box1.hasAttribute("alt");
console.log(hasAlt);
The result is: false
Task 33: Refer to task 27; what is the value of the alt attribute?
let box1 = document.querySelector("#container #box-1");
let altValue = box1.getAttribute("alt");
console.log(altValue);
The result is: null
setAttribute()¶
Task 34: Get the h1 element in the header element. Does h1 has an id tag?
let h1 = document.querySelector("header > h1");
let hasId = h1.hasAttribute("id");
console.log(hasId);
The result is: false
Task 35: Refer to task 34; set the value of the id attribute to #heading1. Hint: use element.setAttribute("id", "heading1").
let h1 = document.querySelector("header > h1");
h1.setAttribute("id", "heading1");
console.log(h1);
console.log(h1.getAttribute("id"));
The result is as follows:
<h1 id="heading1">Welcome to 3 three magical boxes website</h1>
heading1
element.setAttribute()
The element.setAttribute(attr, attrValue) method sets the given attribute value to a given value.
Task 36: Set the class attribute of the #box-2 element to "box black awesome".
let box2 = document.querySelector("#container > #box-2");
box2.setAttribute("class", "box black awesome");
console.log(box2);
console.log(box2.getAttribute("class"));
The result is as follows:
<div class="box black awesome" id="box-2"></div>
box black awesome
removeAttribute()¶
Task 37: Remove the class attribute from #box-3. Hint: use element.removeAttribute("class").
let box3 = document.querySelector("#container > #box-3");
box3.removeAttribute("class");
console.log(box3);
The result is: <div id="box-3"></div>
element.removeAttribute()
The element.removeAttribute(attr) method removes the given attribute from the element.
Task 38: Remove the id attribute from the container element.
let container = document.querySelector("#container");
container.removeAttribute("id");
console.log(container.getAttribute("id"));
The result is: null
Task 39: Remove the class attribute from all the boxes.
let boxes = document.querySelectorAll("#container > .box");
for(let box of Array.from(boxes)){
box.removeAttribute("class");
}
console.log(boxes);
The result is: NodeList(3) [div#box-1, div#box-2, div#box-3]
Task 40: Remove the id attribute from all the boxes.
let boxes = document.querySelectorAll("#container > .box");
for(let box of Array.from(boxes)){
box.removeAttribute("id");
}
console.log(boxes);
The result is: NodeList(3) [div.box, div.box, div.box]